
Many of the data we use today is linked to physical locations. As a result, geospatial intelligence is practical knowledge that necessitates not only the display of location data but also a thorough understanding of where things are, why they are there, and what is likely to occur in a given location. We can solve real-world problems by collecting spatial data and applying critical spatial analytics.
This is referred to as location intelligence in the business world. It’s referred to as GEOINT in the defense industry. Regardless of the name, geospatial intelligence is used to harness spatial data through spatial analytics and reasoning.
What Exactly is Geographic Intelligence?
GEOINT is the short form for GEOspatial Intelligence. It’s about using images and info about places to understand what’s happening on Earth. This field includes making maps, analyzing images, and studying the details of Earth from above.
Geospatial Intelligence (GEOINT) is about utilizing geography to comprehend what’s happening in various locations. It examines data such as maps from satellites, aircraft, GPS, and even census statistics to determine what is happening in specific locations. This type of intelligence was formerly reserved for the government and military. But it is increasingly being used by other countries and corporations.
It covers many different things, like mapping, analyzing images, and figuring out info from pictures. Even though it was used mainly by the military, now, it’s used by other groups too. Including companies working in things like phones, transportation, health, safety, and real estate to improve life.
The main idea behind GEOINT is to gather all the info about places on Earth and use it to make stuff that helps planners, emergency workers, and decision-makers do their jobs better.
Brief History About GEOINT
GEOINT hasn’t been around for too long, but the idea of using pictures from above goes way back. Around the early 1900s, the military started using aerial photos to get info. It took off during the World Wars, becoming a specialized area called Imagery Intelligence (IMINT). During the Cold War, the US and the Soviet Union were big players in this game, watching each other closely.
Things got even more interesting when the space race started in the late 1950s. The Soviet Union launched the first satellite, opening up new ways to watch what’s happening on Earth. The US then launched its satellites, like the CORONA program, getting tons of pictures of places like the USSR and China. During the Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962, an imaging analyst named Dino Brugioni showed how important this intelligence was for keeping countries safe.
After 1991, things picked up with more advanced satellites, a growing commercial market, and new agencies focused on this kind of intelligence. The formation of groups like the National Imagery and Mapping Agency (NIMA), the US National Geospatial Agency, and the European Union Satellite boosted GEOINT to where it is today.
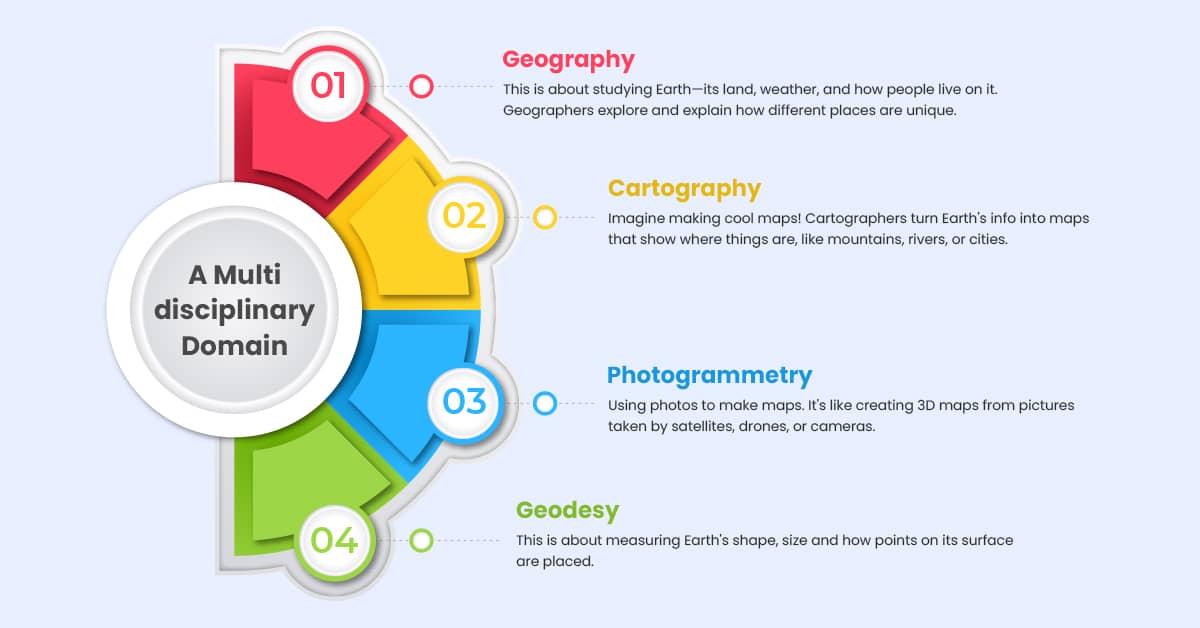
A Multidisciplinary Domain
GEOINT is considerably more than just satellite picture analysis. It is more of an overall framework capable of evaluating and graphically synthesizing the material acquired by Human material (HUMINT), Signal Intelligence (SIGINT), and IMINT than a separate intelligence tradecraft.
All the pieces Geography, Cartography, Photogrammetry, Geodesy, and GIS—fit together in GEOINT. They help us learn about our planet, make smart choices, and solve problems in many different areas, like keeping countries safe, planning cities, farming better, and caring for the environment. GEOINT is like a big picture that helps us understand what’s happening on Earth.
Geospatial Intelligence (GEOINT) is made of different pieces that help us learn about our planet. Let’s look at these aspects:
Geography:
This is about studying Earth its land, weather, and how people live on it. Geographers explore and explain how different places are unique.
Cartography:
Imagine making cool maps! Cartographers turn Earth’s info into maps that show where things are, like mountains, rivers, or cities.
Photogrammetry:
Using photos to make maps. It’s like creating 3D maps from pictures taken by satellites, drones, or cameras.
Geodesy:
This is about measuring Earth’s shape and size and how points on its surface are placed.
Now, there’s a Geographic Information System (GIS). It’s like a computer tool that helps gather, organize, and study all this information about Earth. It’s a valuable toolbox that helps us make maps, understand landscapes, and see how different things connect in different places.
How to Enhance Geointelligence Capabilities
Making Geointelligence better means improving how we collect, analyze, and use information about locations to make smarter decisions. Geointelligence, or geospatial intelligence, involves using data about places to understand things more broadly.
Here are some strategies to make Geointelligence better:
- Advanced Geospatial Data Collection:
Use better tools like satellites, aerial surveys, LiDAR, and drones to collect more accurate and timely location data.
- Integration of Multi-Source Data:
Combine information from various sources like satellites, maps, social media, and smart devices. This helps us see the big picture of what’s happening in a specific place.
- Enhanced Remote Sensing Technologies
Keep up with new technologies that help us sense and understand places better. This includes tools that can see different types of light or capture more details.
- Big Data Analytics:
Use big data techniques to process and understand large amounts of location data quickly. This helps us see patterns and trends as they happen.
- Machine Learning and AI Algorithms:
Teach computers to learn and understand location data on their own. This means they can find patterns, spot unusual things, and predict what might happen next.
6. Cloud-Based Solutions:
Use internet-based platforms to analyze and store location data. This makes it easier to share and work with this data efficiently.
7. Interoperability Standards
Stick to rules that make different systems and tools work together smoothly. This ensures that everyone uses the same language when talking about location data.
- Geospatial Visualization Tools:
Make location data more understandable with advanced tools. This includes making 3D maps, interactive dashboards, and even using augmented reality to see data in the real world.
- Geospatial Mobile Apps :
Create or use apps on mobile devices to collect and send location data in real-time. This helps when we need quick information in fast-changing situations.
- Cybersecurity Measures:
Make sure that location data is safe from unauthorized access, changes, or disruptions. Since location data can be sensitive, good security is crucial.
- Cross-Agency Collaboration:
Encourage different groups and organizations to share data, knowledge, and tools. This helps everyone better understand what’s happening in different places.
Major Components of GEOINT
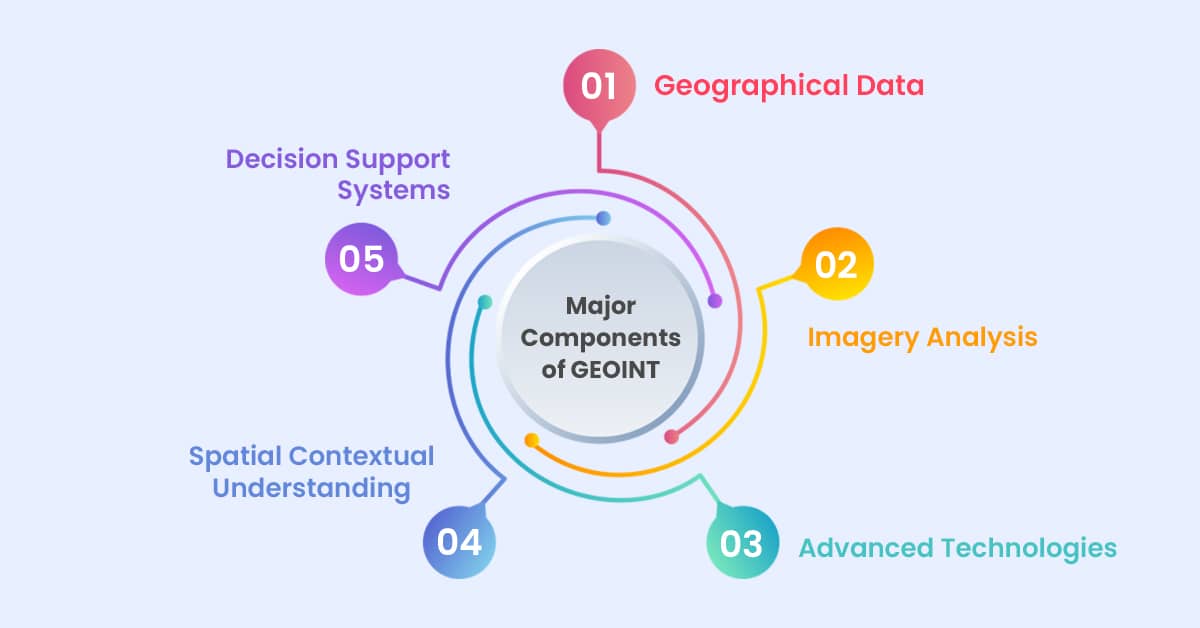
Geospatial Intelligence (GEOINT) relies on several critical components that work together to provide comprehensive insights. By putting the components together, GEOINT helps us understand what places are like and makes it easier for people to make important decisions.
1. Geographical Data:
Think of this as the puzzle’s backbone. It’s made up of maps, pictures from satellites, models of landscapes, and big collections of location info. All these pieces of data give us lots of details about places and what they look like.
2. Imagery Analysis:
This piece involves looking at pictures closely. It could be photos from satellites, planes, or even drones. People who study GEOINT examine these pictures to find any changes, patterns, or strange things in specific places.
3. Advanced Technologies:
Imagine having super-smart tools like computers that learn, artificial intelligence, and systems that help manage geographic info. These tools help a lot because they make it faster and easier to study vast amounts of data about places.
4. Spatial Contextual Understanding:
GEOINT isn’t just about numbers and facts—it’s about understanding how things relate to each other in different places. It’s like seeing the bigger picture and understanding how everything in a place connects and interacts. This is super important for making sense of all the data we collect.
5. Decision Support Systems:
GEOINT is a guide that helps people make wise choices in many different areas. It uses all the info it gathers to help plan things, check risks, handle disasters, improve cities, improve military operations, and much more.
The Future Outlook for Geospatial Intelligence
1. Smarter Computers:
Nowadays, computers are learning to do more things on their own. In GEOINT, this means machines handling tasks like figuring out data without needing lots of human help. This helps finish work faster and makes the analysis accurate.
2. Extra Info in Real Life:
Imagine looking around and seeing more than what’s there. In GEOINT, this could be like adding maps or details on top of what you see. It makes understanding maps and info about places more fun and more accessible.
3. Instant Updates:
Right now, info takes time to process and understand. But in the future, we’ll get it as it happens. It’s like having live updates on what’s going on in different places. This means we can make decisions faster and react quickly to what’s happening.
Technological Advancements Driving Geospatial Intelligence
The technologies speed up how fast we understand stuff, making it quicker and more accurate. The idea is to make decisions in different fields based more on data. With these improvements, GEOINT is making it easier to make smart choices using lots of good geographic information. New technology makes Geospatial Intelligence (GEOINT) much better.
1. Cloud Computing:
It’s like keeping all your stuff on your computer and the internet so that you can reach it from anywhere. For GEOINT, this means handling lots of data like maps and pictures in a more accessible manner. Analysts can store, work on, and share this data better. It’s like having all the essential info at your fingertips.
2. Internet of Things (IoT):
This means connecting different gadgets to the internet to get real-time data. In GEOINT, IoT helps gather new info about places, like weather or traffic data. This real-time info gives a more accurate picture of what’s happening in different spots.
3. Spatial Modeling Techniques:
This is about making detailed models of areas. GEOINT helps create excellent models showing what places look like or how people move around there. These models help to understand how things are connected, making analyses better.
Conclusion
Geospatial Intelligence (GEOINT) is an essential tool in today’s world, especially with tons of data everywhere. GEOINT is not just a tool; it’s a facilitator of informed decisions and strategic planning. It enables authorities to predict, mitigate, and respond to challenges efficiently in defense, disaster management, or sustainable development.
Think of it as a big key that helps us make intelligent choices in many different ways. It’s not just about one thing but involves many areas. For example, it’s used to keep countries safe, plan cities better, handle emergencies like disasters, and even take care of the environment.
Its impact is huge, spreading across many fields. This shows how crucial it is in helping us make decisions in our modern world, filled with information. GEOINT is like a guiding light, helping us navigate the sea of data to make better choices in various aspects of life.


